Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication: A Comprehensive Guide
Machining and sheet metal fabrication are essential manufacturing processes used to create parts, components, and structures for various industries. While both methods involve manipulating materials, they do so in different ways. Machining typically refers to the removal of material using tools like lathes, mills, and drills, while sheet metal fabrication focuses on shaping and assembling metal sheets into usable products through cutting, bending, and forming.
These techniques are fundamental in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction, and more. From custom machine parts to intricate metal designs, machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n provide precision, durability, and customization for a wide range of applications.
The Basics of Machining
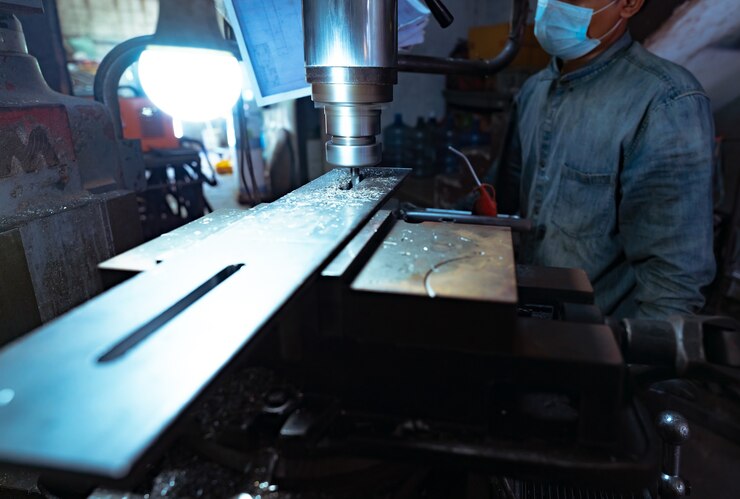
Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves removing material from a workpiece to create the desired shape. It can be performed on metals, plastics, wood, and other materials. There are various machining techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and CNC machining. These processes use specialized tools to cut, shape, and finish the material with extreme precision.
One of the most common tools in machining is the CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine, which automates the process, ensuring accuracy and consistency. CNC machines follow programmed instructions to produce complex parts with tight tolerances, making them ideal for industries requiring high-quality components.
Key Machining Techniques
- Turning: Involves rotating the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material, typically performed on a lathe.
- Milling: A process that uses rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece.
- Drilling: Creating holes in a workpiece using a drill bit.
- Grinding: A finishing process where an abrasive wheel smooths the surface of a material.
- CNC Machining: Computer-controlled machines that automate the machining process for precision and efficiency.
What is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Sheet metal fabricatio’n is a manufacturing process that shapes and assembles metal sheets into finished products. It involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal pieces into the required form. Unlike machining, which removes material, sheet metal fabrication manipulates the material without significantly altering its mass.
This process is highly versatile and is used to create a wide range of products, from simple brackets and enclosures to complex machinery and architectural structures. Sheet metal fabricatio’n is widely utilized in industries like construction, electronics, HVAC, and automotive manufacturing.
Key Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques
- Cutting: Shearing, laser cutting, and water jet cutting are common methods used to cut metal sheets into specific shapes.
- Bending: Metal sheets are bent using presses or brakes to achieve the desired angles and forms.
- Forming: The metal is shaped into a three-dimensional object using dies and punches.
- Welding and Assembly: Various welding techniques are used to join metal parts together, creating a finished product.
Benefits of Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication
Both machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n offer numerous advantages that make them integral to modern manufacturing. Understanding their benefits can help businesses choose the right process for their needs.
Precision and Accuracy
Machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n allow for high precision and accuracy, especially when using CNC technology. These processes can produce parts with tight tolerances, ensuring that components fit perfectly in their applications.
Customization
Both methods offer a high degree of customization. Machining can create complex geometries and detailed features, while sheet metal fabrication allows for custom shapes, sizes, and assemblies. This flexibility makes them ideal for creating bespoke products or prototyping.
Durability
The materials used in these processes, such as steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, are known for their strength and durability. Machined and fabricated parts can withstand harsh conditions, making them suitable for demanding industries like aerospace and construction.
Cost-Effectiveness
Machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n can be cost-effective for both small and large production runs. CNC machining reduces labor costs by automating the process, while sheet metal fabrication can efficiently produce parts in high volumes.
Versatility
From tiny precision parts to large structural components, machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n can accommodate a wide range of sizes, materials, and designs. This versatility makes them suitable for various industries and applications.
Industries that Rely on Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication
Many industries depend on machining and sheet metal fabrication to produce essential components and products. These processes play a critical role in manufacturing, construction, and technology sectors, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, machining and sheet metal fabrication are used to create complex engine parts, airframe components, and support structures. These processes ensure that aerospace products meet strict safety and performance standards.
Automotive
Machining and sheet metal fabrication are vital in the automotive sector, where they produce everything from engine parts to body panels. The precision and durability of these processes contribute to the performance and longevity of vehicles.
Electronics
The electronics industry relies on sheet metal fabrication to produce enclosures, brackets, and chassis for electronic devices. Machining is used to create small, precise components for circuits, sensors, and connectors.
Construction
Sheet metal fabrication is essential in construction for creating metal frames, ductwork, roofing, and other structural elements. Machining is often used to produce custom parts for specialized construction equipment.
Medical Devices
Medical device manufacturing requires precision and reliability, making machining and sheet metal fabrication crucial. These processes are used to create surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment with the utmost accuracy.
Choosing Between Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication
When deciding between machining and sheet metal fabrication, it’s important to consider the requirements of your project. Each process has its strengths and limitations, depending on factors like material, design complexity, production volume, and cost.
Design Complexity
For intricate designs with detailed features or small components, machining is often the best choice. CNC machines can produce highly complex geometries with precision. On the other hand, sheet metal fabrication is ideal for producing larger, simpler shapes and assemblies.
Material Selection
Both machining and sheet metal fabrication can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. However, some materials are more suited to one process over the other. Machining is better for harder materials, while sheet metal fabrication works well with thinner, flexible materials like aluminum or steel sheets.
Production Volume
If you need a large volume of parts quickly, sheet metal fabrication may be more efficient, especially for large, simple designs. Machining is typically more time-consuming but can produce highly detailed parts, making it better suited for low-volume or specialized production runs.
Cost Considerations
The cost of each process depends on factors like material, labor, and production time. Machining can be more expensive due to the time and precision required, but CNC technology has made it more affordable for small and medium-sized production runs. Sheet metal fabrication tends to be more cost-effective for larger production volumes.
Advances in Machining and Sheet Metal Fabrication Technology
Technology continues to evolve in both machining and sheet metal fabrication, driving improvements in speed, precision, and capabilities. Automation, digital design, and new materials have revolutionized these industries, making it easier to produce high-quality parts efficiently.
CNC Machining Advancements
CNC machines have become faster, more precise, and capable of handling complex tasks. With the integration of AI and machine learning, CNC machining can now optimize cutting paths and reduce waste, further improving efficiency.
Laser and Water Jet Cutting
In sheet metal fabrication, laser cutting and water jet cutting have become popular methods for achieving clean, precise cuts without damaging the material. These technologies allow for faster production and greater flexibility in design.
Additive Manufacturing
While machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n are subtractive processes, additive manufacturing (3D printing) is becoming an increasingly valuable complementary technique. In some cases, 3D printing can be combined with machining or fabrication to create hybrid components, reducing material waste and increasing design flexibility.
Conclusion
Machining and sheet metal fabrication are two of the most important manufacturing processes in modern industry. Both techniques offer unique advantages in terms of precision, durability, and customization. From small, intricate components to large structural assemblies, machining and sheet metal fabrication enable the creation of high-quality products across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and construction.
With continuous advancements in technology, these processes are becoming more efficient, allowing manufacturers to produce superior products faster and at a lower cost. Whether you’re looking to create a single prototype or mass-produce components, understanding the capabilities of machining and sheet metal fabrication will help you choose the best solution for your project.
FAQs
What is the difference between machining and sheet metal fabrication?
Machining is a subtractive process that removes material to create precise parts, while sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets into a final product.
Which industries use machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n ?
These processes are used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, construction, and medical device manufacturing.
What materials are used in machining and sheet metal fabricatio’n ?
Common materials include metals like aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and brass, as well as plastics and composites.
How does CNC machining improve the process?
CNC machining automates the process, increasing precision, consistency, and efficiency, making it ideal for producing complex parts with tight tolerances.
What are the benefits of sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication offers versatility, cost-effectiveness, and durability, making it suitable for producing a wide range of products in high volumes.