Decoding Gender Development Index: A Comprehensive Explanation
Welcome to our blog post where we dive deep into the fascinating world of gender development! Today, we will be exploring the Gender Development Index (GDI) and decoding its meaning. Whether you are a passionate advocate for gender equality or simply curious about how countries measure up in terms of empowering women and girls, this article is for you.
The GDI is an essential tool that provides insights into the progress made towards achieving gender equality on a global scale. It goes beyond traditional measures of development by incorporating key indicators specifically tailored to assess gender disparities. Join us as we unravel the complexities of this index, analyze its results, and understand its implications for human development.
So grab your metaphorical magnifying glass as we embark on this enlightening journey through the intricacies of the Gender Development Index. Let’s uncover what lies beneath these numbers and discover how they shape societies worldwide. Are you ready? Let’s get started!
Understanding the Gender Development Index (GDI)
Understanding the Gender Development Index (GDI) is crucial in comprehending the progress and disparities between genders worldwide. The GDI provides a comprehensive measure of gender development by assessing various factors that contribute to gender equality. It goes beyond simply measuring income or education levels, taking into account key components such as health, education, and economic participation.
The Gender Development Index evaluates these components based on specific indicators within each category. For example, in terms of health, it considers life expectancy at birth for both males and females. In education, it measures indicators like literacy rates among adults and enrollment rates for primary, secondary, and tertiary education. Economic participation is assessed through indicators such as labor force participation rates for both men and women.
With this holistic approach to measuring gender development, the GDI provides valuable insights into the progress made towards achieving gender equality globally. By analyzing GDI scores across countries and regions, we can identify areas where significant disparities exist between genders. This allows policymakers to target interventions more effectively to address these inequalities and create policies that promote inclusivity and equal opportunities for all individuals regardless of their gender identity or expression.
In conclusion:
Overall,
Understanding the Gender Development Index helps us gain a deeper understanding of how different societies are progressing towards achieving gender equality. By focusing on multiple dimensions of development – from health to education to economic participation – the GDI offers a comprehensive view of gender disparities around the world. Through targeted policies and interventions guided by GDI findings, we can work towards creating a more equitable society where everyone has equal opportunities for growth and development.
Definition of the Gender Development Index
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is a vital tool used to measure and analyze gender disparities across countries. It provides valuable insights into the development status of men and women within a society, helping policymakers identify areas for improvement. The GDI goes beyond mere economic indicators by incorporating social factors that contribute to gender inequality.
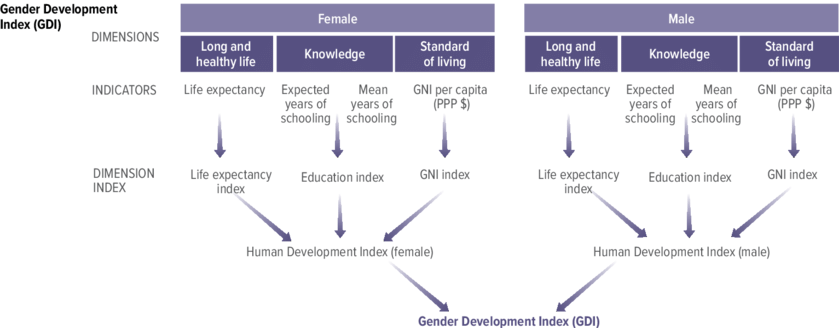
At its core, the GDI measures three key dimensions: health, education, and income. By considering these aspects, it offers a comprehensive understanding of how gender affects human development. The GDI takes into account indicators such as life expectancy at birth for males and females, mean years of schooling for both genders, and estimated earned income per capita.
This index allows us to delve deeper into the complexities of gender inequality by shedding light on various facets of development experienced by different genders. It aims to uncover discrepancies in access to healthcare, educational opportunities, employment prospects, and overall quality of life between men and women. With this information in hand, policymakers can design targeted interventions that address specific challenges faced by each gender group.
Key Components and Indicators of the GDI
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is a comprehensive measure that assesses the level of gender development in different countries. It takes into account several key components and indicators to provide a holistic view of gender equality and empowerment.
One of the key components considered in the GDI is education. Education plays a crucial role in empowering women and narrowing gender gaps. The indicator used to measure this component is the mean years of schooling for adult women, which reflects their access to quality education. Additionally, the expected years of schooling for girls are also taken into account, highlighting the importance of ensuring equal educational opportunities from an early age.
Another important component included in the GDI is health. This component focuses on indicators such as life expectancy at birth for females compared to males, as well as maternal mortality rates. These indicators shed light on disparities in healthcare access and highlight areas where improvements are needed to ensure better overall health outcomes for women.
Furthermore, economic participation and decision-making power form another significant aspect considered within the GDI framework. Indicators such as labor force participation rate for women and proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments help determine gender disparities when it comes to economic opportunities and political representation.
These key components and indicators provide valuable insights into various aspects of gender development worldwide. By analyzing these factors collectively, policymakers can identify areas where progress has been made or where interventions are necessary to promote greater gender equality and empowerment globally.
Analyzing GDI Results and Findings
Exploring GDI Scores Worldwide
When it comes to analyzing the Gender Development Index (GDI), a global perspective is essential. By examining GDI scores worldwide, we gain valuable insights into the state of gender development across different countries and regions.
From Scandinavia to Sub-Saharan Africa, the variations in GDI scores paint a vivid picture of gender disparities and progress. Some nations boast impressive rankings, with high levels of gender equality in areas such as education and health. Others struggle with significant gaps between men and women when it comes to access to resources and opportunities.
Gender Disparities and Progress
Delving deeper into the findings of the Gender Development Index uncovers both encouraging progress and persistent challenges. While there have been notable improvements in certain aspects of gender development, disparities still exist in various dimensions.
The GDI provides crucial data on income inequality, educational attainment, reproductive health indicators, political representation, and more. These indicators enable us to track progress over time while identifying areas where targeted interventions are needed.
By analyzing these results critically, policymakers can develop evidence-based strategies that address specific barriers faced by women worldwide. The aim is not only to bridge existing gaps but also to foster an inclusive society where everyone has equal opportunities for personal growth and flourishing.
Remember: Analyzing GDI results isn’t about drawing conclusive statements or generalizing entire populations based on their scores alone; rather it’s about using this information as a starting point for informed discussions around gender equality initiatives at local, national, regional levels – leading towards sustainable change!
Exploring GDI Scores Worldwide
When it comes to understanding gender development, the Gender Development Index (GDI) provides valuable insights into the progress and disparities experienced by women around the world. By analyzing GDI scores on a global scale, we can gain a deeper understanding of how different countries fare in terms of gender equality.
From Scandinavian nations known for their progressive policies to developing countries striving for social change, GDI scores reveal a complex tapestry of advancements and challenges. These scores highlight where improvements have been made in areas such as education, health, and employment opportunities for women. They also shed light on regions where significant gender disparities persist despite efforts towards inclusivity.
In short, exploring GDI scores worldwide allows us to see the diverse landscape of gender development across nations. It serves as an important tool in identifying areas that require further attention and support in order to achieve true equality for all individuals irrespective of their gender identity or expression.
Gender Disparities and Progress
Understanding gender disparities is essential for assessing the progress of societies in achieving gender equality. The Gender Development Index (GDI) provides valuable insights into these disparities by measuring key indicators related to education, health, and income.
The GDI scores worldwide reflect the varying degrees of gender inequality across different countries. While some nations have made significant strides towards reducing gender disparities, others still face significant challenges in ensuring equal opportunities for men and women. These discrepancies highlight the need for targeted interventions and policies to address gender inequalities effectively.
In recent years, there have been notable improvements in certain areas such as access to education and healthcare for women. However, persistent gaps remain in various regions concerning income parity and representation in leadership roles. Achieving true gender equality requires not only addressing these existing disparities but also creating an inclusive environment that values diversity and promotes equal opportunities for all individuals regardless of their gender identity or expression.
By analyzing the GDI results on a global scale, policymakers can identify patterns of progress or stagnation when it comes to achieving gender equality goals. This information can inform policy decisions aimed at promoting sustainable development while ensuring that no one is left behind due to their gender. It is crucial to recognize that progress cannot be achieved through isolated efforts; rather, it requires comprehensive strategies involving multiple stakeholders working together towards a common goal.
As we delve deeper into understanding the implications of the GDI on human development, we must acknowledge that there is still much work ahead. By acknowledging existing disparities and taking proactive steps towards eliminating them, societies can foster an environment where everyone has equal rights and opportunities – irrespective of their gender identity or expression.
Comparing GDI and Gender Inequality Index (GII)
When it comes to measuring gender equality and development, two important indices come into play: the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Inequality Index (GII). While both aim to assess gender disparities, they approach the issue from different angles.
The GDI focuses on three key dimensions – health, education, and income. It provides a comprehensive overview of how well women are faring in these areas compared to men. On the other hand, the GII takes a broader perspective by incorporating indicators such as maternal mortality rates, adolescent birth rates, political representation, and empowerment measures. This index aims to capture not only inequalities but also structural barriers that hinder women’s progress.
Both indices play crucial roles in understanding gender inequality across countries. By analyzing their results side by side, policymakers can gain valuable insights into specific areas where progress is needed most urgently. Moreover, comparing these indices allows for a more nuanced understanding of gender disparities at various levels – be it within regions or globally.
Overview of the Gender Inequality Index
The Gender Inequality Index (GII) is a crucial tool for measuring gender disparities and analyzing the progress of women in various aspects of life. It provides an overview of the inequalities between men and women across different dimensions, such as reproductive health, empowerment, and labor market participation.
By examining indicators like maternal mortality rates, educational attainment, and political representation, the GII paints a comprehensive picture of gender inequality worldwide. The index highlights areas where women face significant challenges and barriers to their development, shedding light on societal norms that perpetuate discrimination. With its multidimensional approach, the GII offers valuable insights into the complexities of gender inequality that cannot be captured by traditional economic measures alone.
Different Dimensions and Indicators in GDI and GII
When it comes to measuring gender development and inequality, two key indexes come into play: the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Inequality Index (GII). While both provide valuable insights, they focus on different dimensions and indicators.
The GDI takes a multidimensional approach by considering three main components: health, education, and income. It measures these dimensions using indicators such as life expectancy at birth for females compared to males, expected years of schooling for females compared to males, and gross national income per capita for females compared to males. By examining these factors together, the GDI provides a comprehensive view of gender disparities in human development.
On the other hand, the GII delves deeper into various aspects that contribute to gender inequality. It looks beyond just health, education, and income to include dimensions like reproductive health empowerment and economic participation. The indicators used in the GII include maternal mortality ratio, adolescent birth rate, parliamentary seats held by women versus men, labor force participation rate among women versus men, among others. This broader scope allows for a more nuanced understanding of gender inequalities across different societies.
These contrasting approaches highlight how each index offers unique perspectives on gender development and inequality. While the GDI focuses on overall human development outcomes related to health, education,and income,the GII zooms in on specific areas where women face particular challenges,such as reproductive rightsand economic empowerment.
The combinationofthese indicesprovides policymakers witha morecomprehensivepictureofgenderinequalityinordertoinform targeted interventionsand policiesfor achieving true equalitybetween genders.
Inthe questforprogress,it is crucialtoacknowledgethese distinctdimensionsandindicatorsin orderto addressgenderdisparitieseffectively
Evaluating GDI and GII for Gender Development Analysis
When it comes to assessing gender development and equality, two important indices come into play: the Gender Development Index (GDI) and the Gender Inequality Index (GII). While both provide valuable insights, they approach the subject from different angles.
The GDI focuses on measuring gender disparities in three key dimensions: health, education, and income. It takes into account indicators such as life expectancy, literacy rates, and earned income. On the other hand, the GII offers a more comprehensive view by considering additional factors like reproductive health and empowerment. By evaluating these indices side by side, we can gain a deeper understanding of gender development trends across countries.
By breaking down each dimension within these indices, policymakers can identify areas that require attention or improvement. This analysis allows for targeted interventions that address specific challenges faced by women in various societies. Additionally, comparing the results of both indices helps us assess where progress has been made in reducing gender inequalities over time.
Analyzing both the GDI and GII provides a holistic picture of gender development worldwide. It enables us to uncover patterns and trends that may not be apparent when looking at one index alone. By delving into their respective dimensions and indicators, we can better comprehend how far we have come in achieving true gender equality – while also recognizing how much work remains to be done.
Implications of GDI on Human Development
The Gender Development Index (GDI) plays a crucial role in assessing gender equality and its implications on human development. By measuring key indicators such as health, education, and income, the GDI provides valuable insights into the progress made towards achieving gender parity.
These findings have significant implications for policymakers and organizations working towards improving gender equality. The GDI serves as a powerful tool to identify areas where interventions are needed the most. With this knowledge, policies can be tailored to address specific challenges faced by women in different regions or countries. By focusing on improving GDI scores, societies can create equal opportunities for both men and women to thrive in all aspects of life.
Moreover, the GDI also highlights the importance of investing in education and healthcare for women. It underscores how empowering women through education not only benefits them individually but also has far-reaching effects on society as a whole. When women are provided with equal access to quality education and healthcare services, they are better equipped to contribute meaningfully to their communities and drive economic growth.
In summary:
– The GDI’s implications extend beyond statistics; they shape policy decisions.
– Addressing disparities highlighted by the index leads to targeted interventions.
– Investing in education empowers women individually while benefiting society at large.
By recognizing these implications, governments and organizations can work together towards creating an inclusive society that values gender equality as an essential component of overall human development.
Role of GDI in Assessing Gender Equality
The Gender Development Index (GDI) plays a crucial role in assessing gender equality on a global scale. By examining key indicators such as education, health, and income. The GDI provides valuable insights into the progress and disparities faced by women in different countries.
One of the primary functions of the GDI is to highlight areas where gender equality has been achieved or where significant gaps still exist. It allows policymakers and researchers to identify specific challenges. That need to be addressed in order to promote equal opportunities for all individuals regardless of their gender. The GDI also serves as a powerful tool for advocating for policies and interventions. That can help improve gender development outcomes.
In addition, the GDI helps shed light on how societal norms and cultural practices impact women’s well-being across different regions. It reveals patterns of inequality within societies, enabling stakeholders to understand the underlying factors contributing to these disparities. With this knowledge, governments and organizations can develop targeted strategies aimed at empowering women economically, socially, and politically.
By providing an accurate assessment of gender development levels worldwide through its comprehensive set of indicators. The GDI contributes significantly towards achieving sustainable development goals related to gender equality. Its data-driven approach ensures that efforts are focused on addressing specific areas requiring improvement while recognizing achievements made so far. Understanding the role of GDI in assessing gender equality is essential for fostering inclusive societies. That provide equal opportunities for everyone irrespective of their gender identity or expression.
Policies and Interventions to Improve GDI Scores
Policies and interventions play a crucial role in improving GDI scores and promoting gender development. Governments, organizations, and communities must implement targeted measures to address the disparities. And challenges faced by women across various dimensions of development.
One key policy is ensuring equal access to education for both genders. This can be achieved through initiatives such as scholarships. Incentives for girls’ education, and the removal of barriers that hinder their participation in schools. Additionally, policies should focus on enhancing women’s economic empowerment by providing vocational training opportunities. Promoting entrepreneurship among women, and ensuring fair wages and decent working conditions. By addressing these areas, societies can create an enabling environment where women have the resources and opportunities to thrive.
Through comprehensive policies that promote gender equality in healthcare services, governments can improve GDI scores. Accessible healthcare facilities with specialized programs targeting women’s health issues are essential. Furthermore, reproductive rights should be protected to ensure that women have control over their bodies. And can make informed decisions about their health. Policies addressing violence against women are also vital in improving GDI scores; strict laws need to be enacted alongside awareness campaigns aimed at challenging societal norms that perpetuate gender-based violence.
Conclusion
Understanding the Gender Development Index (GDI) is crucial in comprehending the progress made towards achieving gender equality and women’s empowerment. This comprehensive measurement tool provides valuable insights into various indicators. Such as education, health, and income, that contribute to gender development.
Through analyzing GDI results worldwide, we can identify areas where gender disparities persist and track improvements over time. These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions and policies to address these inequalities effectively.
Comparing the GDI with other indices like the Gender Inequality Index (GII). Allows us to gain a more holistic understanding of gender development. While both indices assess different dimensions of inequality. They complement each other in providing a comprehensive picture of gender disparities globally.
The implications of the GDI on human development are significant. By assessing gender equality through this index, policymakers can make informed decisions about resource allocation. And prioritize interventions aimed at improving overall well-being for all genders.
To improve GDI scores globally, it is essential to implement policies. That promote equal access to education and healthcare for all individuals. Additionally, addressing socio-cultural norms that perpetuate discrimination against women is vital for creating an inclusive society. That values diversity and promotes equal opportunities for everyone.