Understanding the Root Hair Cell Diagram: A Key to Plant Nutrition
Welcome to the fascinating world of plant nutrition! Have you ever wondered how plants absorb essential nutrients from their environment? Today, we’re going to delve into a crucial aspect of this process – root hair cell. These tiny, but mighty structures play a vital role in the uptake and transport of water and nutrients in plants.
Understanding the root hair cell diagram is like unlocking the secret code to plant nutrition. By grasping its intricate details and functions, we gain valuable insights into how plants thrive and grow. So, let’s embark on this journey together as we explore the significance, structure, development, modifications, and functions of these remarkable cellular components.
Prepare to be amazed by the hidden wonders within each plant’s roots as we unravel the mysteries behind root hair cells. Whether you have a green thumb or simply appreciate nature’s marvels, this article will provide you with a deeper appreciation for the complex mechanisms that support plant life.
Significance of Root Hair Cells in Plant Nutrition
Root hair cells play a crucial role in the nutrition of plants. These tiny, elongated structures are found on the surface of plant roots and are responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Without root hair cells, plants would struggle to take up essential minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
The significance of root hair cells lies in their ability to increase the surface area of roots, allowing for more efficient nutrient absorption. The long and slender shape of these cells enables them to penetrate into small spaces between soil particles, maximizing contact with water and mineral ions. This specialized adaptation is vital for plants’ survival as it ensures they can access the necessary resources required for growth and development.
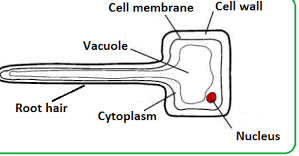
Overview of the Root Hair Cell Diagram
Root hair cells play a crucial role in plant nutrition, and understanding their structure is essential to grasp the complexity of this process. The root hair cell diagram provides an overview of these specialized cells that are responsible for nutrient uptake from the soil. In this diagram, we can see the unique features and adaptations that make root hair cells so effective at absorbing water and nutrients.
The root hair cell diagram illustrates the elongated shape of these cells, resembling tiny hairs extending from the root surface. These microscopic structures increase the surface area available for nutrient absorption. Additionally, they possess thin walls with numerous projections called trichoblasts that further enhance their absorptive capacity. This detailed illustration allows us to visualize how these cellular structures work together to optimize nutrient uptake in plants.
Occurrence and Dimensions of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells are a crucial part of plant anatomy, playing a vital role in nutrient absorption. These specialized cells can be found in the roots of most vascular plants, allowing them to efficiently take up water and nutrients from the surrounding soil. Root hair cells are tiny structures, with diameters ranging from 10 to 20 micrometers. Despite their small size, they greatly increase the surface area of the root system, enabling plants to maximize nutrient uptake.
These microscopic extensions protrude from the surface of the root epidermis and can be observed under a microscope as delicate elongated structures. The length of root hairs varies depending on various factors such as plant species and environmental conditions but typically ranges between 50 to 500 micrometers long. This allows for increased contact with soil particles, enhancing nutrient absorption capabilities. Their slender shape also aids in penetrating into small crevices within the soil structure, further facilitating efficient nutrient uptake by plants.
Where Root Hair Cells are Found in Plants
Root hair cells are a vital part of plant anatomy, playing a crucial role in nutrient absorption and water uptake. These specialized cells can be found primarily near the tips of plant roots, where they extend into the surrounding soil. They have an elongated shape with numerous tiny projections called root hairs that greatly increase their surface area for efficient nutrient absorption.
These root hair cells are typically located in the zone of maturation, which is closer to the tip of the root. As new cells are continuously produced at the root apex, older mature cells near the tip differentiate into these specialized structures. This strategic positioning ensures that plants can maximize their ability to extract essential nutrients from the surrounding soil and absorb water effectively.
Size and Structure of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells play a crucial role in absorbing water and nutrients for the growth and development of plants. These specialized cells are found in the roots of plants, specifically in the region known as the root hair zone. In terms of size, root hair cells are relatively long and slender, resembling tiny hairs or projections that extend from the surface of the root.
The structure of a root hair cell consists of a single elongated tube-like projection with a large surface area. This unique shape allows for increased absorption capacity by maximizing contact with soil particles and water. The outer layer of these cells is made up of thin cell walls that facilitate the movement of substances into the cell. Inside, there is a cytoplasmic layer containing various organelles responsible for essential cellular functions such as nutrient uptake and transport.
Structure and Development of Root Hair Cells
Anatomy plays a crucial role in understanding the structure and development of root hair cells. These specialized cells are found on the surface of plant roots, extending like tiny fingers into the soil to absorb water and nutrients. At first glance, they may appear simple, but upon closer examination, their intricate design becomes evident.
Root hair cells have a unique structure that allows them to fulfill their vital function. They consist of a long tubular projection called a root hair, which arises from an epidermal cell in the root cortex. This elongated structure increases the surface area available for nutrient absorption. The tip of each root hair is covered with fine microvilli-like extensions known as trichoblasts or trichomes. These microscopic projections further enhance nutrient uptake by increasing contact with soil particles.
The development of root hair cells occurs in stages. It begins with cell differentiation within the meristematic region near the tip of growing roots. As these specialized cells mature, they extend outwards towards the soil through elongation and growth processes regulated by various hormones such as auxin and ethylene. This complex process ensures that plants can effectively establish connections with their environment for optimal nutrition.
Anatomy of a Root Hair Cell
The anatomy of a root hair cell is fascinating and crucial to understanding how plants absorb nutrients from the soil. These specialized cells are found in the epidermis of plant roots and play a vital role in nutrient uptake.
At first glance, root hair cells appear as thin, elongated projections that extend from the surface of the main root. They have a large surface area due to their long and narrow shape, which allows for increased absorption of water and minerals. The tip of each root hair cell contains an extension called the rhizoid, which further enhances its ability to penetrate into small crevices within the soil.
Inside these remarkable cells, there are several important structures at work. The cytoplasm fills most of the cell’s interior space and houses various organelles such as mitochondria for energy production and vacuoles for storage purposes. A central nucleus controls cellular functions while numerous tiny hairs known as microvilli line the outer surface to facilitate nutrient absorption.
These intricate details contribute to the efficient functioning of root hair cells, enabling them to take up essential elements necessary for plant growth and development. Understanding their anatomy provides valuable insights into how plants acquire nutrients from their surrounding environment.
Stages of Root Hair Cell Development
The development of root hair cells is a fascinating process that takes place in plants. It involves several distinct stages, each contributing to the formation of functional root hairs.
The initiation stage begins with the specification of certain epidermal cells as potential root hair cells. These selected cells then undergo elongation and differentiation into specialized structures known as trichoblasts. The next stage is expansion, where trichoblasts continue to grow and extend outwards from the root surface, eventually forming long, slender projections called root hairs.
As these stages progress, various molecular signals and genetic factors play crucial roles in guiding the development of root hair cells. Understanding this intricate process provides valuable insights into how plants acquire nutrients from their surroundings and adapt to different environmental conditions.
Modifications and Functions of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells are not just ordinary plant cells. They possess unique adaptations that enable them to efficiently absorb water and nutrients from the soil. One key adaptation is their elongated shape, which increases the surface area available for absorption. This allows root hair cells to maximize their contact with the surrounding soil particles and enhance nutrient uptake.
In addition, root hair cells have thin cell walls and numerous projections called root hairs. These features further increase the surface area for absorption, allowing them to capture more water and nutrients from the soil solution. The presence of these specialized structures makes root hair cells highly efficient in their role as absorptive units within plants’ roots.
The primary function of root hair cells is nutrient acquisition from the soil. By absorbing essential minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients like iron and zinc, these specialized cells play a crucial role in supporting plant growth and development. Additionally, root hair cells also take up water through osmosis.
By absorbing water along with vital nutrients, they ensure an adequate supply of moisture to all parts of the plant’s body. This process helps maintain turgidity (rigidity) in plant tissues while facilitating various physiological activities such as photosynthesis and transpiration.
Special Adaptations of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells have unique adaptations that enable them to efficiently absorb water and nutrients from the soil. One of their notable adaptations is the presence of elongated projections called root hairs, which greatly increase the surface area for absorption. These microscopic extensions are so thin that they can penetrate between soil particles, allowing roots to explore a larger volume of soil.
In addition to their shape, root hair cells also possess a high concentration of transport proteins in their plasma membrane. These proteins facilitate the movement of ions and molecules into the cell, ensuring efficient nutrient uptake. Furthermore, root hairs have a specialized outer layer known as the rhizodermis, which contains suberin—a waxy substance that helps prevent water loss through evaporation. This adaptation allows plants to retain moisture in dry environments and ensures optimal functioning of root hair cells in nutrient absorption.
Functions and Roles of Root Hair Cells in Plant Nutrition
Root hair cells play vital functions and hold crucial roles in the nutrition of plants. These tiny, finger-like extensions found on the surface of root tips absorb essential nutrients from the soil, such as water and minerals. The numerous root hairs significantly increase the surface area available for absorption, allowing plants to efficiently uptake these necessary resources.
The primary function of root hair cells is to absorb water and minerals from the soil through a process called osmosis. Water moves into the roots due to an imbalance in concentration between the inside of the cell and its surroundings. This process ensures that plants have sufficient hydration for growth and other metabolic activities. Additionally, root hair cells also facilitate nutrient uptake by absorbing ions like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and more. These nutrients are vital for various plant processes such as photosynthesis, protein synthesis, energy production, and overall growth development.
Transport Mechanisms Utilizing Root Hairs
Different Pathways for Nutrient Absorption
Root hairs play a crucial role in the absorption of nutrients by plants. They provide an extensive surface area that enhances the plant’s ability to uptake essential elements from the soil. But how exactly do these root hairs transport nutrients? Well, there are different pathways involved in this process.
One pathway is called apoplastic transport, where nutrients move through the cell walls and intercellular spaces between cells. Another pathway is symplastic transport, which involves movement through plasmodesmata – small channels connecting adjacent cells. Both of these pathways work together to ensure efficient nutrient absorption by root hairs. So it’s safe to say that root hair cells serve as important conduits for transporting vital substances throughout the plant system.
Role of Root Hair Cells in Water and Nutrient Uptake
Apart from their involvement in nutrient absorption, root hair cells also play a significant role in water uptake by plants. The thin-walled structure and elongated shape of these cells enable them to penetrate deep into the soil, reaching areas with higher moisture content. Through osmosis, water enters the root hair cells and then moves towards other parts of the plant via specialized tissues like xylem vessels.
Additionally, root hair cells also assist in taking up ions such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and more from the soil solution surrounding them. These nutrients are essential for various metabolic processes within plants including growth, flowering, fruiting etc., so having well-developed and functional root hairs is crucial for overall plant health and productivity.
Different Pathways for Nutrient Absorption
When it comes to nutrient absorption in plants, root hair cells play a vital role. These tiny structures have specialized pathways that allow them to efficiently absorb nutrients from the soil. There are different pathways through which these essential elements can enter the root hair cells.
One pathway is called passive diffusion, where nutrients move from an area of high concentration to low concentration without requiring any energy input. Another pathway is facilitated diffusion, where specific carrier proteins help transport certain ions across the cell membrane. Both of these mechanisms ensure that plant roots can take up nutrients effectively and meet their nutritional needs for growth and development.
In addition to these pathways, there is also active transport, which requires energy expenditure by the root hair cell. This process involves the use of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to pump ions against their concentration gradient into the cell. Active transport allows plants to take up essential minerals even when they are present in low concentrations in the soil.
Understanding these different pathways for nutrient absorption helps us appreciate how intricate and efficient plant systems are at obtaining vital elements from their surroundings. Root hair cells truly are remarkable structures that enable plants to thrive in various environments!
Role of Root Hair Cells in Water and Nutrient Uptake
Root hair cells play a crucial role in the uptake of water and nutrients by plants. These tiny, finger-like extensions on the surface of root hairs greatly increase the surface area available for absorption. Through their intricate structure and selective permeability, root hair cells are able to actively transport ions, minerals, and water from the soil into the plant.
In terms of water uptake, root hair cells have specialized aquaporins that allow for rapid movement of water molecules across their cell membranes. This enables plants to maintain proper hydration levels even in dry conditions. Additionally, these cells also absorb essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other micronutrients through various transport mechanisms like active transport or facilitated diffusion. This ensures that plants receive all the necessary elements for growth and development.
Life Span and Maintenance of Root Hair Cells
Growth and Lifespan of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells, like any other living cells, have a finite lifespan. They are constantly being produced at the root tips and eventually die off as they mature. This continuous cycle ensures that there is a constant supply of functional root hairs for nutrient absorption.
Factors Influencing Root Hair Cell Maintenance
Several factors can influence the maintenance of root hair cells. One important factor is the availability of nutrients in the soil. If there is an abundance of nutrients, it can stimulate the growth and development of new root hairs. However, if there is a lack of essential nutrients, it may lead to the shedding or premature aging of existing root hairs. Additionally, environmental conditions such as temperature and moisture levels play a role in determining how long root hair cells survive.
Growth and Lifespan of Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells play a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. These specialized cells form small, finger-like projections that extend from the surface of plant roots. The growth of root hair cells is a continuous process, as new cells are constantly being produced to replace older ones.
The lifespan of a root hair cell varies depending on various factors such as environmental conditions and nutrient availability. On average, these cells have a relatively short lifespan ranging from a few days to several weeks. During their lifespan, root hair cells undergo rapid growth and expansion to increase their surface area for nutrient absorption. This constant turnover ensures that plants have an efficient system for nutrient uptake from the soil.
Factors Influencing Root Hair Cell Maintenance
Root hair cells play a crucial role in the nutrient uptake of plants. But their lifespan and maintenance can be influenced by various factors. One key factor is the availability of nutrients in the surrounding soil. If there is an abundance of essential minerals. Root hair cells may not need to grow as extensively or live as long.
Additionally, environmental conditions such as temperature and moisture levels can impact root hair cell maintenance. Extreme temperatures or drought can stress the plant, leading to decreased root hair cell production and survival. Similarly, excessive moisture or waterlogging can disrupt oxygen supply to the roots, affecting root hair cell health.
It’s worth noting that genetic factors also come into play when it comes to maintaining healthy root hair cells. Some plant species naturally have longer-lived and more efficient root hairs than others due to their specific genetic makeup. Understanding these factors is vital for optimizing plant nutrition and ensuring healthy growth through proper care and management strategies.
Summary and Conclusion
In this article, we have delved into the fascinating world of root hair cells and their crucial role in plant nutrition. Root hair cells are specialized structures found in the roots of plants. Responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. By understanding the root hair cell diagram, we gain valuable insights into how these cells function and contribute to overall plant health.
Root hair cells occur near the tips of young roots, where they extend outwards like tiny hairs. Despite their small size, they play a significant role in nutrient uptake by increasing the surface area available for absorption. These elongated structures can vary in shape and dimensions depending on the specific plant species.
The anatomy of a root hair cell consists of several important components that facilitate its functions. From an elongated structure with a thin wall to numerous projections called trichoblasts, each part contributes to efficient nutrient absorption. The development stages of root hair cells involve differentiation from specialized epidermal cells into mature structures capable of nutrient uptake.
Root hair cells exhibit interesting modifications and adaptations that enhance their ability to absorb nutrients efficiently. These include increased surface area through branching or swelling at certain points along its lengt. As well as secretion of enzymes to break down complex molecules into simpler forms for easier absorption.
Transport mechanisms involving root hairs are vital for plants’ survival. Nutrient absorption occurs through various pathways such as passive diffusion or active transport systems across cell membranes. Water uptake is also facilitated by osmosis through root hairs.